Aquaculture and the Conservation of Endangered Species
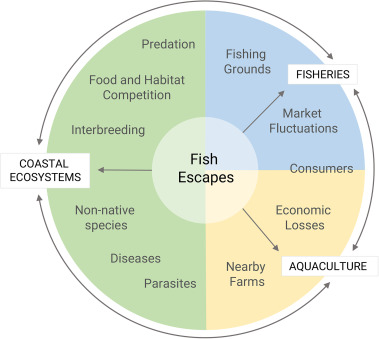
In an era of growing environmental awareness and a sense of responsibility for preserving our planet’s biodiversity, the intersection of aquaculture and endangered species conservation has never been more relevant. This timely connection has found a supporter in the form of a forward-thinking company dedicated to producing dry pelletized fish food from recycled paper.
As the world faces the urgent need to conserve endangered aquatic species, the innovative approach of EcoFeed Aquaculture Solutions to fish food production offers hope for conservation. By addressing critical environmental issues and providing nutritional value to aquatic organisms, this company embodies the principles of sustainable aquaculture and conservation.
Here’s why the convergence of aquaculture and the conservation of endangered species is a significant stride toward ecological preservation:
The Decline of Endangered Aquatic Species
The decline of many aquatic species has been accelerated by various factors, including habitat destruction, overfishing, pollution, and climate change. As a result, numerous species find themselves on the brink of extinction. Among these are iconic creatures like sea turtles, sturgeon, various species of coral, and several types of freshwater fish. Without intervention, the loss of these species could disrupt the balance of aquatic ecosystems and lead to far-reaching consequences.
The Role of Aquaculture in Conservation
Aquaculture steps in as a conservation tool by focusing on the breeding and rehabilitation of endangered aquatic species. Here are several ways in which aquaculture contributes to conservation efforts:
-
Breeding and Reintroduction Programs
Many endangered species have difficulty reproducing in the wild due to various threats. Aquaculture facilities provide a controlled environment where these species can be bred successfully. The offspring can then be reintroduced into their natural habitats, bolstering their populations.
-
Captive Assurance Populations
Aquaculture serves as a safety net by maintaining captive assurance populations of endangered species. These populations act as genetic reservoirs, reducing the risk of extinction in the wild due to unforeseen events.
-
Research and Monitoring
Aquaculture provides valuable insights into the biology and ecology of endangered species. Researchers can closely study these species in controlled settings, which helps in developing effective conservation strategies.
-
Reducing Pressure on Wild Populations
By producing endangered species in aquaculture settings, the demand for their wild-caught counterparts decreases, reducing the pressure on their natural populations.
Success Stories in Aquaculture Conservation
Several success stories highlight the positive impact of aquaculture on the conservation of endangered species. For example:
- Sea Turtles: Sea turtle hatcheries in various parts of the world help protect and release hatchlings to increase their chances of survival.
- Sturgeon: Sturgeon aquaculture has led to the production of caviar and meat while reducing the demand for wild-caught sturgeon, which are often targeted for their valuable roe.
- Coral Restoration: Coral farming techniques are being developed to restore damaged coral reefs and protect vulnerable coral species.
Challenges and Considerations
While aquaculture plays a vital role in endangered species conservation, it is not without challenges. Maintaining genetic diversity in captive populations, disease management, and the potential for unintentional hybridization are among the issues that require careful attention.
In addition, the ethical and ecological implications of releasing captive-bred individuals into the wild must be thoroughly considered to ensure successful reintegration and long-term survival.
The Future of Aquaculture and Conservation
As we move forward in the 21st century, the partnership between aquaculture and the conservation of endangered species is poised to grow stronger. Ongoing research, technological advancements, and international cooperation will enable aquaculture to continue its valuable contributions to the preservation of our planet’s aquatic biodiversity.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the synergy between aquaculture and endangered species conservation embodies a holistic approach to conservation. The use of waste paper in fish feed production, touching on both the nutritional and ecological aspects of aquatic life, highlights the vital link between sustainable aquaculture and species conservation. As the world looks for ways to protect the planet’s most vulnerable species, this innovative solution becomes a symbol of hope for the future of our oceans and the magnificent creatures that inhabit them.